Wire Rope Inspection and Removal from Service Criteria
Do you know what to look for when inspecting a wire rope, crane rope, or wire rope cable assembly? This article provides inspection and removal criteria for wire rope.
The following is a fairly comprehensive listing of critical inspection factors. It is not, however, presented as a substitute for an experienced inspector. It is rather a user’s guide to the accepted standards by which wire ropes must be judged. Use the outline to skip to specific sections:
- 1. Abrasion
- 2. Rope Stretch
- Phase 1
- Phase 2
- Phase 3
- 3. Reduction in Rope Diameter
- 4. Corrosion
- 5. Kinks
- 6. Doglegs
- 7. “Bird Caging”
- 8. Localized Conditions
- 9. Heat Damage
- 10. Protruding Core
- 11. Damaged End Attachments
- 12. Peening
- 13. Scrubbing
- 14. Fatigue Fracture
- 15. Broken Wires
- 16. Electric Arc
- Replacement Criteria for Rotation Resistant Ropes
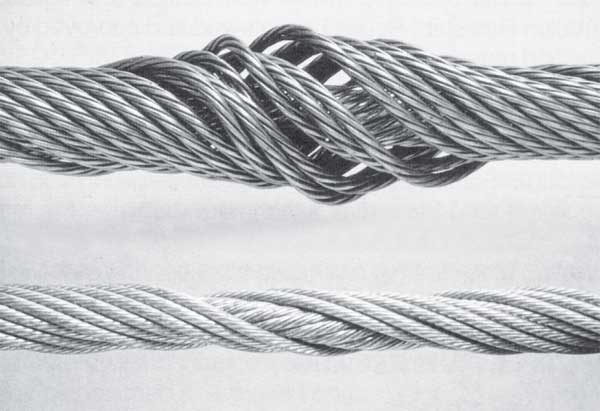
1. Abrasion
Rope abrades when it moves through an abrasive medium or over drums and sheaves. Most standards require that rope is to be removed if the outer wire wear exceeds 1/3 of the original outer wire diameter. This is not easy to determine, and discovery relies upon the experience gained by the inspector in measuring wire diameters of discarded ropes.
2. Rope Stretch
All ropes will stretch when loads are initially applied. As a rope degrades from wear, fatigue, etc. (excluding accidental damage), continued application of a load of constant magnitude will produce incorrect varying amounts of rope stretch.
Phase 1
Initial stretch, during the early (beginning) period of rope service, caused by the rope adjustments to operating conditions (constructional stretch).
Phase 2
Following break-in, there is a long period—the greatest part of the rope’s service life—during which a slight increase in stretch takes place over an extended time. This results from normal wear, fatigue, etc.
Phase 3
Thereafter, the stretch occurs at a quicker rate. This means that the rope has reached the point of rapid degradation: a result of prolonged subjection to abrasive wear, fatigue, etc. This second upturn of the curve is a warning indicating that the rope should soon be removed.
3. Reduction in Rope Diameter
Any marked reduction in rope diameter indicates degradation. Such reduction may be attributed to:
- Excessive external abrasion
- Internal or external corrosion
- Loosening or tightening of rope lay
- Inner wire breakage
- Rope stretch
- Ironing or milking of strands
In the past, whether or not a rope was allowed to remain in service depended to a great extent on the rope’s diameter at the time of inspection. Currently, this practice has undergone significant modification.
Previously, a decrease in the rope’s diameter was compared with published standards of minimum diameters. The amount of change in diameter is, of course, useful in assessing a rope’s condition. But, comparing this figure with a fixed set of values can be misleading.
These long accepted minimums are not, in themselves, of any serious significance since they do not take into account such factors as:
- Variations in compressibility between IWRC and fiber core
- Differences in the amount of reduction in diameter from abrasive wear, or from core compression, or a combination of both
- The actual original diameter of the rope rather than its nominal value
As a matter of fact, all ropes will show a significant reduction in diameter when a load is applied. Therefore, a rope manufactured close to its nominal size may, when it is subjected to loading, be reduced to a smaller diameter than that stipulated in the minimum diameter table. Yet under these circumstances, the rope would be declared unsafe although it may, in actuality, be safe.
As an example of the possible error at the other extreme, we can take the case of a rope manufactured near the upper limits of allowable size. If the diameter has reached a reduction to nominal or slightly below that, the tables would show this rope to be safe. But it should, perhaps, be removed.
Today, evaluations of the rope diameter are first predicated on a comparison of the original diameter—when new and subjected to a known load—with the current reading under like circumstances. Periodically, throughout the life of the rope, the actual diameter should be recorded when the rope is under equivalent loading and in the same operating section. This procedure, if followed carefully, reveals a common rope characteristic: after an initial reduction, the diameter soon stabilizes. Later, there will be a continuous, albeit small, decrease in diameter throughout its life.
Core deterioration, when it occurs, is revealed by a more rapid reduction in diameter and, when observed, it is time for removal.
Deciding whether or not a rope is safe is not always a simple matter. A number of different but interrelated conditions must be evaluated. It would be dangerously unwise for an inspector to declare a rope safe for continued service simply because its diameter had not reached the minimum arbitrarily established in a table if, at the same time, other observations lead to an opposite conclusion.
Because criteria for removal are varied, and because diameter, in itself, is a vague criterion, the table of minimum diameters has been deliberately omitted from this manual.
4. Corrosion
Corrosion, while difficult to evaluate, is a more serious cause of degradation than abrasion. Usually, it signifies a lack of lubrication. Corrosion will often occur internally before there is any visible external evidence on the rope surface.
Pitting of wires is a cause for immediate rope removal. Not only does it attack the metal wires, but it also prevents the rope’s component parts from moving smoothly as it is flexed. Usually, a slight discoloration because of rusting merely indicates a need for lubrication.
Severe rusting, on the other hand, leads to premature fatigue failures in the wires necessitating the rope’s immediate removal from service. When a rope shows more than one wire failure adjacent to a terminal fitting, it should be removed immediately. To retard corrosive deterioration, the rope should be kept well lubricated with a clear wire rope lube that can penetrate between strands. In situations where extreme corrosive action can occur, it may be necessary to use galvanized wire rope.
5. Kinks
Kinks are tightened loops with permanent strand distortion that result from improper handling when a rope is being installed or while in service. A kink happens when a loop is permitted to form and then is pulled down tight, causing permanent distortion of the strands. The damage is irreparable and the sling must be taken out of service.
6. Doglegs
Doglegs are permanent bends caused by improper use or handling. If the dogleg is severe, the sling must be removed from service. If the dogleg is minor, exhibiting no strand distortion and cannot be observed when the sling is under tension, the area of the minor dogleg should be marked for observation and the sling can remain in service.
7. “Bird Caging”
Bird caging results from torsional imbalance that comes about because of mistreatment, such as sudden stops, the rope being pulled through tight sheaves, or wound on too small a drum. This is cause for rope replacement unless the affected section can be removed.
8. Localized Conditions
Particular attention must be paid to wear at the equalizing sheaves. During normal operations, this wear is not visible. Excessive vibration or whip can cause abrasion and/or fatigue. Drum cross-over and flange point areas must be carefully evaluated. All end fittings, including splices, should be examined for worn or broken wires, loose or damaged strands, cracked fittings, worn or distorted thimbles and tucks of strands.
9. Heat Damage
After a fire or the presence of elevated temperatures, there may be metal discoloration or an apparent loss of internal lubrication. Fiber core ropes are particularly vulnerable. Under these circumstances the rope should be replaced.
10. Protruding Core
If, for any cause, the rope core protrudes from an opening between the strands, the rope is unfit for service and should be removed.
11. Damaged End Attachments
Cracked, bent or broken end fittings must be eliminated. The cause should be sought out and corrected. In the case of bent hooks, the throat openings—measured at the narrowest point—should not exceed 5%, not to exceed 1/4″ opening and any visibly apparent bend or twist from the plane of the unbent hook over normal nor should twisting be greater than 10°.
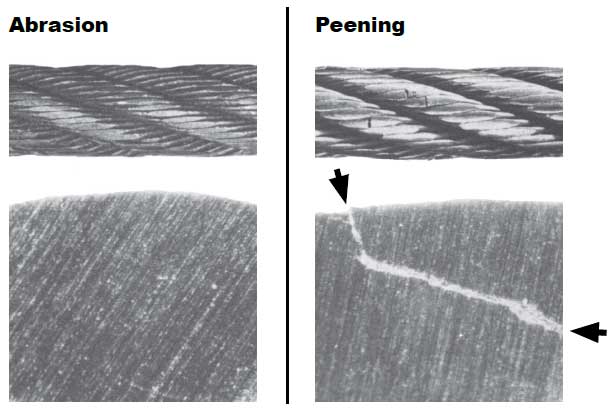
12. Peening
Continuous pounding is one of the causes of peening. This can happen when the rope strikes against an object, such as some structural part of the machine, or it beats against a roller or it hits itself. Often, this can be avoided by placing protectors between the rope and the object it is striking.
Another common cause of peening is continuous working-under high loads—over a sheave or drum. Where peening action cannot be controlled, it is necessary to have more frequent inspections and to be ready for earlier rope replacement.
Below are plain views and cross-sections show effects of abrasion and peening on wire rope. Note that a crack has formed as a result of heavy peening.
13. Scrubbing
Scrubbing refers to the displacement of wires and strands as a result of rubbing against itself or another object. This, in turn, causes wear and displacement of wires and strands along one side of the rope. Corrective measures should be taken as soon as this condition is observed.
14. Fatigue Fracture
Wires that break with square ends and show little surface wear have usually failed as a result of fatigue. Such fractures can occur on the crown of the strands or in the valleys between the strands where adjacent strand contact exists. In almost all cases, these failures are related to bending stresses or vibration.
If diameter of the sheaves, rollers or drum cannot be increased, a more flexible rope should be used. But, if the rope in use is already of maximum flexibility, the only remaining course that will help prolong its service life is to move the rope through the system by cutting off the dead end. By moving the rope through the system, the fatigued sections are moved to less fatiguing areas of the reeving.
15. Broken Wires
The number of broken wires on the outside of a wire rope are an index of its general condition, and whether or not it must be considered for replacement. Frequent inspection will help determine the elapsed time between breaks. Ropes should be replaced as soon as the wire breakage reaches the numbers given in the chart below. Such action must be taken without regard to the type of fracture.
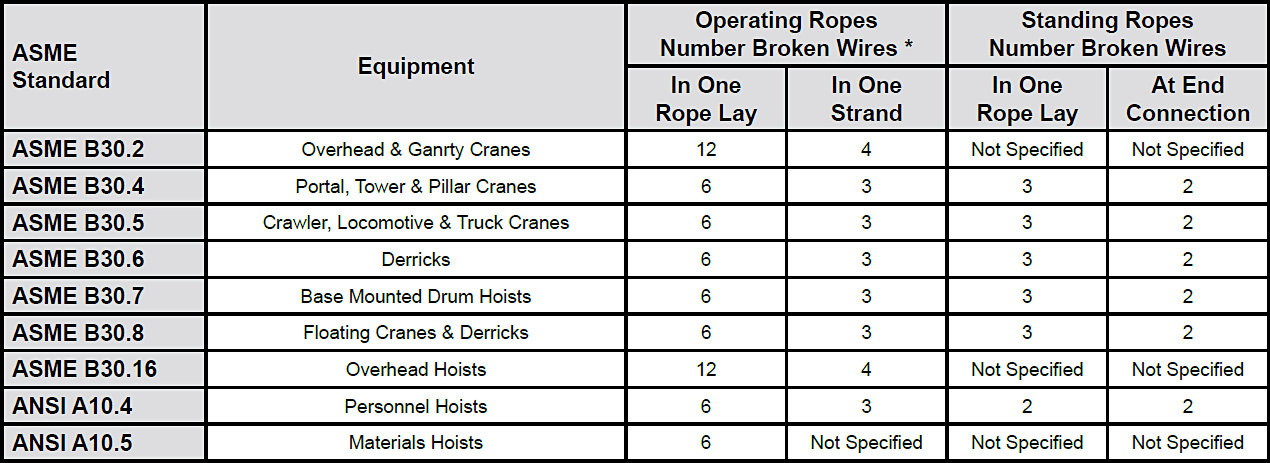
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
* All ropes in the above applications—one outer wire broken at the point of contact with the core that has worked its way out of the rope structure and protrudes or loops out of the rope structure. Additional inspection of this section is required.
16. Electric Arc
Rope that has either been in contact with a live power line or been used as “ground” in an electric welding circuit, will have wires that are fused, discolored and/or annealed and must be removed.
On occasion, a single wire will break shortly after installation. However, if no other wires break at that time, there is no need for concern. On the other hand, should more wires break, the cause should be carefully investigated.
On any application, valley breaks—where the wire fractures between strands—should be given serious attention. When two or more such fractures are found, the rope should be replaced immediately. (Note, however, that no valley breaks are permitted in elevator ropes.)
It is good to remember that once broken wires appear—in a rope operating under normal conditions—a good many more will show up within a relatively short period. Attempting to squeeze the last measure of service from a rope beyond the allowable number of broken wires (refer to table on the next page) will create an intolerably hazardous situation.
A diagnostic guide to some of the most prevalent rope abuses are given on the following pages—these abuses are illustrated and described.
Replacement Criteria for Rotation Resistant Ropes
Recommended retirement criteria for all Rotation Resistant Ropes are 2 broken wires in 6 rope diameters or 4 broken wires in 30 rope diameters (i.e. 6 rope diameters for a 1″ diameter rope = 6″).
Distortion of Rotation Resistant Ropes, as shown below, can be caused by shock load / sudden load release and/or induced torque, and is the reason for immediate removal from service.